WHY DOES MY CHEST HURT WHEN I COUGH? FINALLY ANSWERED!
WHY DOES MY CHEST HURT WHEN I COUGH? FINALLY ANSWERED!
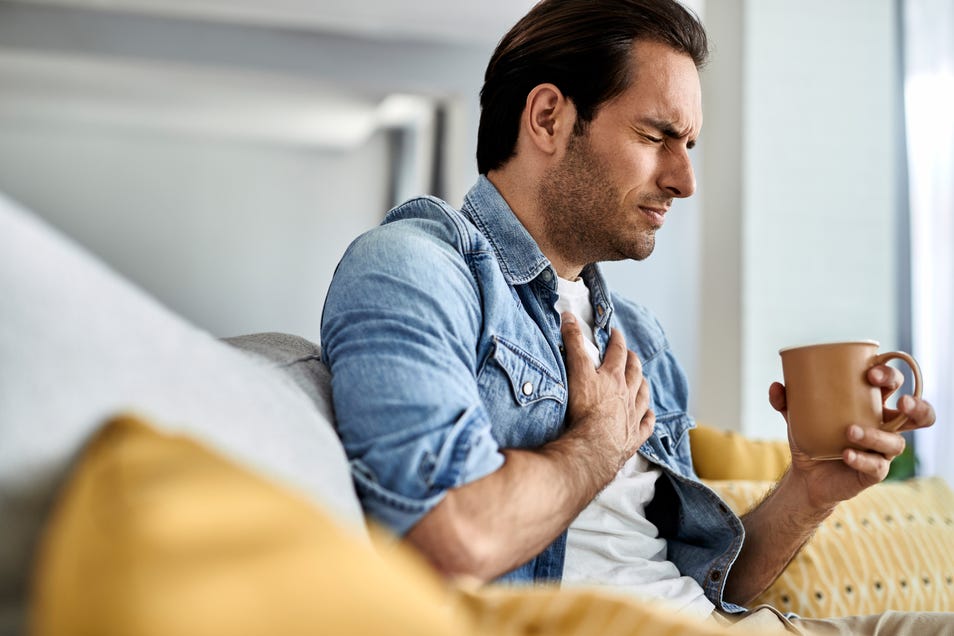

It often starts with a simple cough, your body’s natural way of clearing the throat and airways of irritants, mucus, or germs. At first, it feels harmless, even helpful, as your body protects itself from what doesn’t belong.
However, when coughing becomes frequent or intense, it can take a toll. So, what begins as a mild reflex may soon lead to a sore throat, strained chest muscles, shortness of breath, and eventually sharp or uncomfortable chest pain with every cough.
As time passes, the discomfort becomes increasingly difficult to ignore, and chest pain, in general, typically feels like pressure, tightness, or aching in the chest, often triggered by inflammation, infection, or muscle strain. You may notice that it worsens when you breathe deeply, move suddenly, or cough again.
But don’t worry, Mucinex® Canada is here to guide you through the causes and relief treatments for chest pain when coughing, explained in simple and clear terms.
Causes of chest pain when coughing
Below are some of the most common reasons behind chest pain while coughing.
1. Acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis, often called a chest cold, is the inflammation of the bronchi, the main airways that carry air to your lungs. This swelling can make breathing uncomfortable and irritate the respiratory system and chest.
In acute bronchitis, inflammation and mucus buildup narrow the airways, trapping irritants and causing persistent coughing. This constant strain on chest muscles leads to chest pain, while reduced airflow can make breathing feel heavy or difficult
Some of the most common symptoms of acute bronchitis include:
- Coughing with or without mucus
- Chest soreness
- Mild headache
- Mild fever
- Body aches
2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that affects the lungs, causing the tiny air sacs (alveoli) to become inflamed. It makes breathing more difficult and can cause discomfort in the chest.
Because of this, pneumonia causes a cough as infection and inflammation fill the lungs’ air sacs with fluid, pus, or mucus. This buildup not only irritates the airways but also causes chest pain due to inflammation of lung tissues and the strain of coughing against congested lungs.
Some of the most common symptoms of acute pneumonia include:
- Bacterial infections
- Viral infections
- Fungal infections
- Aspiration of food or liquids
- Weak immune system
3. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic lung condition where the airways become sensitive and react to triggers such as smoke, pollen, or infections. This can make breathing difficult and cause tightness in the chest, making it hard for humans to breathe properly.
As a result, asthma causes chest pain because inflamed and narrowed airways make breathing difficult, straining chest muscles. The buildup of mucus increases pressure, leading to tightness or discomfort, and in severe cases, complications like pneumomediastinum or pneumothorax can cause sharp chest pain.
Common symptoms of asthma include:
- Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander
- Smoke or air pollution
- Respiratory infections such as colds or flu
- Exercise or physical activity
- Strong emotions or stress
4. Pericarditis
Pericarditis happens when the sac-like tissue around your heart, called the pericardium, becomes inflamed. This inflammation can irritate the chest and nearby tissues, sometimes causing sharp pain and affecting normal functions of breathing.
Pericarditis causes chest pain when the inflamed layers of the pericardial sac rub against each other, resulting in sharp or stabbing discomfort that worsens with deep breaths or lying flat. The inflammation or fluid buildup can also press on the heart and surrounding tissues, increasing the severity of the symptoms pain
Some of the most common symptoms of pericarditis include:
- Sudden sharp chest pain (often mistaken for a heart attack)
- Cough
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
5. Flu
The flu is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. It can cause breathing discomfort and often leads to a persistent cough that irritates the chest.
When you have the flu, inflammation in the airways and chest muscles can cause soreness or pain, especially with frequent coughing. The buildup of thick mucus and pressure in the lungs contributes to this discomfort, causing the chest to feel tight or achy.
Some of the most common symptoms of the flu include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Headache
6. Common Cold
The common cold is a mild infection of the upper respiratory tract, affecting the nose and throat. Rhinoviruses usually cause it, though over 200 different viruses can trigger it.
During a common cold, chest pain can occur due to frequent coughing that strains the chest muscles. The buildup of mucus and mild airway inflammation can also create pressure or tightness, leading to discomfort while breathing or coughing.
Some of the most common symptoms of the common cold include:
- Congestion (stuffy nose)
- Chest tightness
- Mild hacking cough
- Scratchy, tickly throat
- Sneezing
7. Acid Reflux (GERD)
Acid reflux is a digestive condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, irritating its lining. This can cause discomfort in the chest and throat, making daily activities uncomfortable.
Acid reflux causes chest pain when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, irritating its lining. This burning sensation, known as heartburn, can feel like sharp or tight pain in the chest, often worsening after eating or when lying down.
Some of the most common symptoms of acid reflux include:
- Heartburn (burning sensation in chest, throat, or stomach)
- Chronic cough
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Regurgitation of food or acid
Cough Treatment
Managing chest pain caused by coughing often involves alleviating irritation, supporting the respiratory system, and addressing the underlying cause. Here are some effective ways to find relief:
1. Home remedies
1. Warm compress on the chest: Applying a warm compress or heating pad to the chest can relax sore muscles and reduce pain caused by coughing.
2. Honey and warm water: Mix honey in warm water or herbal tea to soothe throat irritation and reduce coughing that strains the chest.
3. Ginger tea: Ginger has natural anti-inflammatory properties that help calm chest discomfort and ease coughing.
4. Steam inhalation: Inhaling steam from hot water or herbs helps open airways, loosens mucus, and reduces irritation in the chest.
5. Humidifier use: Using a humidifier keeps indoor air moist, preventing dry air from aggravating chest pain and persistent coughing.
6. Saltwater gargle: Gargling with warm salt water can reduce throat irritation that triggers chest-straining coughs.
2. Over-the-counter medication
When coughing makes your chest ache and every breath feels heavy, Mucinex® Chest Congestion Guaifenesin 600 mg Tablets* works to help loosen mucus.
With its immediate and extended-release bi-layer design, it dissolves fast and releases medicine for up to 12 hours**.
*This product may not be right for everyone. Always read and follow the label.
**600 mg tablets expectorant
FAQs
Can coughing strain my chest muscles?
Yes, persistent or severe coughing can put strain on the muscles in your chest, especially the intercostal muscles between your ribs.
Can a bad cold make your chest hurt when coughing?
A severe cold can cause chest pain when coughing due to inflamed bronchial tubes, a condition known as acute bronchitis or a chest cold. Persistent coughing irritates these areas, leading to soreness, tightness, and discomfort.
Why does my chest hurt when I cough?
Chest pain that occurs when coughing may be caused by muscle strain from the force of coughing, or it could indicate more serious conditions, such as pleurisy, pneumonia, bronchitis, or a pulmonary embolism.
Can allergies or asthma cause chest pain while coughing?
Yes, both asthma and allergies can cause chest pain during coughing because they trigger airway inflammation, constriction, and mucus buildup. Intense coughing from these conditions often leads to chest discomfort, tightness, or a pressing sensation.