CHEST CONGESTION: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, TREATMENT
CHEST CONGESTION: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, TREATMENT
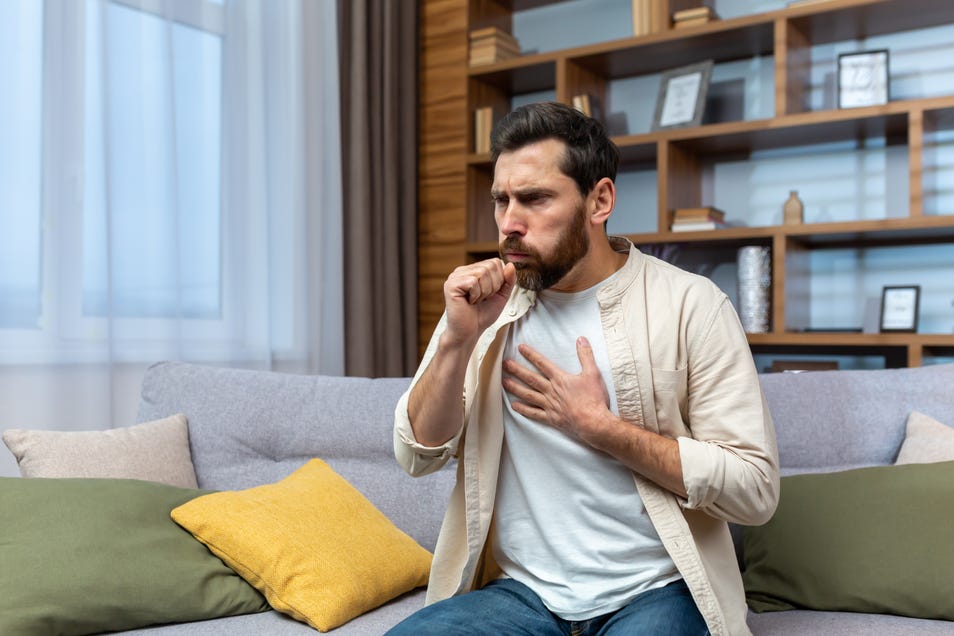

Ever felt like there was a heavy weight pressing down on your chest, making it difficult to breathe or cough properly? That uncomfortable feeling of fullness or heaviness in the chest could be more than just a passing cold; you are likely suffering from chest congestion symptoms.
But what exactly is chest congestion? It is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can range from mild colds to more serious respiratory infections, including bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and influenza.
Understanding what causes it, how to recognize it early, and, most importantly, how to get rid of it effectively can make all the difference in your recovery.
This article covers everything important related to chest congestion for those looking for relief and wanting to breathe more comfortably.
Chest congestion
Chest congestion refers to the buildup of mucus (thicker than usual) in the lungs and lower airways, which makes breathing feel heavy, tight, or labored.
When the airways are inflamed or irritated, the body produces excess mucus to trap and flush out harmful particles, but this can lead to blocked airways, coughing, and discomfort.
Chest congestion can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as wheezing, shortness of breath, a runny nose, sore throat, or chest pain.
Possible causes
Chest congestion can result from various health conditions, including both viral and environmental factors. Some of the most common causes include:
- Respiratory infections: Bronchitis, Bronchiolitis, Pneumonia.
- Common infections: Common cold, COVID-19, Influenza, MAC lung disease, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), Tuberculosis, Whooping cough (pertussis).
- Health conditions: Allergies, Asthma, Cystic fibrosis, Pneumonitis, Genetic diseases such as primary ciliary dyskinesia, inhaling large amounts of dust, as seen with silicosis, and Irritation from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Symptoms
The most common and noticeable symptoms of congestion include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Excess phlegm production
- Fever, headache, sore throat
- Body aches and a stuffy nose
- Chest discomfort (tightness or pressure in the chest)
- Wheezing or crackling sounds in the chest when breathing
Treatment
Medications and home care remedies are typically the primary treatments for chest congestion. However, the treatment varies depending on the underlying condition, with common ones including:- Expectorants that contain guaifenesin, such as Mucinex® Chest Congestion 600 mg Tablets*. It is a bi-layer tablet that dissolves fast & releases medicine for up to 12 hours. It is ideal for relieving chest congestion due to the common cold, as it helps loosen phlegm (mucus) and makes coughs more productive.
- Infection type-specific treatments include antibiotics for bacterial infections and antivirals for viral infections.
- Always consult your healthcare provider before giving over-the-counter cough medicines to children. They can advise you on safety, as many medications are not suitable for children under 6 years old.
*This product may not be right for everyone. Always read and follow the label.
Home remedies
Several home remedies may help relieve symptoms, clear mucus buildup, and treat the underlying cause. Here are some of the most common and effective options:
- Drink warm water, teas, or broths to help break down or thin the mucus present in your throat or lungs.
- Use humidifiers or cool-mist vaporizers to add moisture to the air, which prevents dryness and reduces irritation in the airways.
- Taking adequate rest and staying well-hydrated supports the body’s natural healing process.
- Breathing in warm, moist air helps loosen mucus and makes breathing easier. Adding essential oils like eucalyptus can offer added relief.
If symptoms persist, worsen, or include high fever, consult a healthcare professional. Antibiotics or bronchodilators may be needed in cases of infection or asthma.
FAQs
How long does chest congestion last?
Chest congestion typically lasts between 3 and 7 days but can linger for up to 2 to 3 weeks in some cases, such as with acute bronchitis. If congestion lasts longer than 3 weeks or if other symptoms like fever, wheezing, or shortness of breath develop, it’s recommended to see a healthcare professional.
Is chest congestion contagious?
No, but it often indicates an infection. For example, if your chest congestion results from a cold, flu, or bronchitis, these infections are contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets when someone coughs or sneezes.
How can I prevent chest congestion in the future?
Some of the most common preventive steps include:
- Washing your hands frequently
- Covering coughs and sneezes
- Avoid touching your face
- Drink plenty of fluids (water, tea, broths)
- Minimize exposure to dust, allergens, and smoke